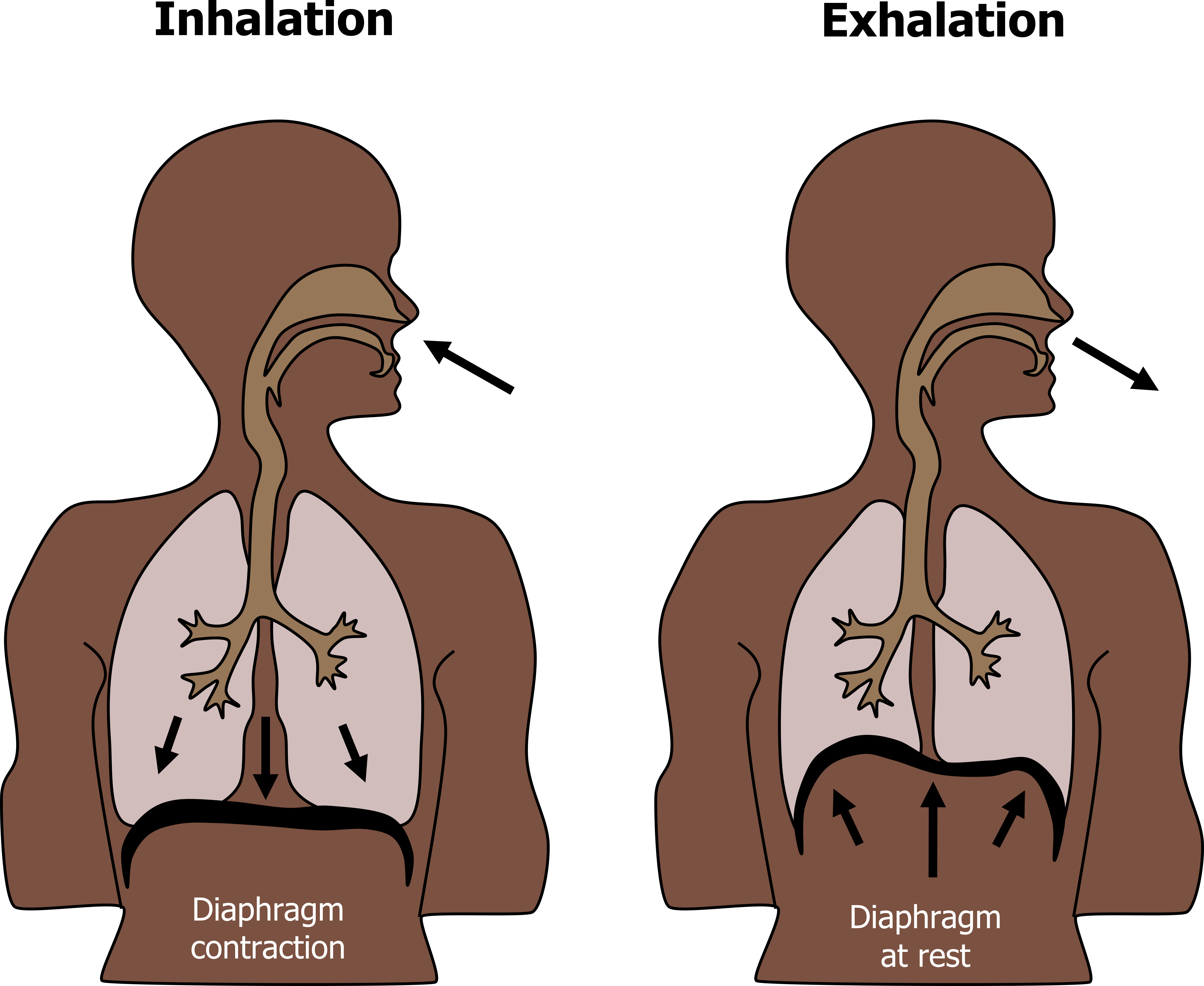
Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation . To equalize the pressure, air enters the. While all other muscles mostly change the. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. This creates more space in. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. during the process of inhalation, the lung volume expands as a result of the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles (the. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward.
from pressbooks.lib.vt.edu
A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. during the process of inhalation, the lung volume expands as a result of the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles (the. While all other muscles mostly change the. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. This creates more space in.
Mechanics of the Lungs Pulmonary Physiology for PreClinical Students
Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. during the process of inhalation, the lung volume expands as a result of the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles (the. While all other muscles mostly change the. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. This creates more space in.
From www.alamy.com
Inhalation diaphragm Stock Vector Images Alamy Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation This creates more space in. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. during the process of inhalation, the lung volume expands as a result of the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles (the. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. when. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.cuh.nhs.uk
Leaflet 3 Breathing techniques to ease breathlessness CUH Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. While all other muscles mostly change the. This creates more space in. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. . Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.researchgate.net
Diaphragmatic breathing. Notes When the patient inhales, the abdominal... Download Scientific Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. during the process of inhalation, the lung volume. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From fastreliefacupuncture.com
Improving the Function of the Diaphragm Fast Relief Acupuncture Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. This creates more space in. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From mammothmemory.net
The diaphragm separates the thorax from the abdomen Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. While all other muscles mostly change the. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.researchgate.net
Normal breathing. Diaphragm expanding into abdomen and rib expansion... Download Scientific Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation To equalize the pressure, air enters the. While all other muscles mostly change the. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. This creates more space in. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From blog.meditopia.com
Discover Diaphragmatic Breathing! Meditopia Blog Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. While all other muscles mostly change the. This creates more space in. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.alamy.com
Lungs inhalation diagram Stock Vector Images Alamy Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. While all other muscles mostly change the. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. To equalize the. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.brainkart.com
Mechanism of breathing Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation To equalize the pressure, air enters the. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. during the process of inhalation, the lung volume expands as a result of the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles (the. This creates more space in. A deep breath,. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.alamy.com
The diaphragm functions in breathing illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. This creates more space in. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.alamy.com
The diaphragm functions in breathing illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. during quiet. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.carlsonstockart.com
Breathing Mechanics Lungs, Ribcage, Diaphragm Carlson Stock Art Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. While all other muscles mostly change the. This creates more space in. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. A. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.flickr.com
Movements of the diaphragm and lungs during inspiration Flickr Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. While all other muscles mostly change the. during a. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.vectorstock.com
Diagram showing diaphragm functions in breathing Vector Image Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. While all other muscles mostly change the. during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. during. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.lihpao.com
How Does the Diaphragm Work? Exploring Anatomy, Physiology, and Treatments The Enlightened Mindset Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. This creates. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From sequencewiz.org
the mechanics of inhalation Sequence Wiz Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From sequencewiz.org
The mechanics of exhalation and the preferred way to exhale in yoga Sequence Wiz Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation during a spasm, the diaphragm doesn’t rise back up after exhalation. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. during quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. the diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. during the process of inhalation, the lung volume expands as a result of the contraction of the diaphragm. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.
From www.geeksforgeeks.org
Inspiration and Expiration Definition, Mechanism, and FAQs Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation when you inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. To equalize the pressure, air enters the. when the diaphragm contracts and moves lower, the chest cavity enlarges, reducing the pressure inside the lungs. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to. during the process of inhalation, the lung volume expands as a result of. Does Diaphragm Move Up During Inhalation.